Correspondent banking facilitates international transactions but poses significant AML risks due to its cross-border nature and lack of transparency. This blog discusses the fundamentals of correspondent banking, associated AML risks, and strategies for mitigating these risks. Key strategies include enhanced due diligence, robust transaction monitoring, regulatory compliance, and regular training and awareness programs.
Correspondent banking is a critical component of the global financial system, which enables one bank to provide cross-border payment services and other financial services to its clients.
However, this intricate network is not without its challenges, particularly concerning Anti-Money Laundering (AML) risks.
In this blog, we will learn the fundamentals of correspondent banking and the AML risks associated with it and provide strategies for financial institutions to mitigate the risks associated with correspondent banking.
What is Correspondent Banking?
Correspondent banking refers to a relationship between two financial institutions, often based in different countries. In this arrangement, one bank (the correspondent) provides services to another bank (the respondent) or the respondent bank’s clients.
These services may include:
- Processing wire transfers
- Currency exchange
- Document collection and other transaction-related services
This arrangement facilitates international financial transactions and global trade, even in countries where the respondent bank has no physical presence.
The Importance of Correspondent Banking
Correspondent banking plays a pivotal role in the global economy.
- It underpins international trade by enabling businesses to transact across borders efficiently.
- For individuals, it facilitates personal transactions like remittances, which are especially vital in economies that heavily rely on funds sent from abroad.
- Maintains a network of relationships with other banks worldwide and provides access to banking and markets beyond national borders.
- Correspondent banking relationships are essential for global financial stability.
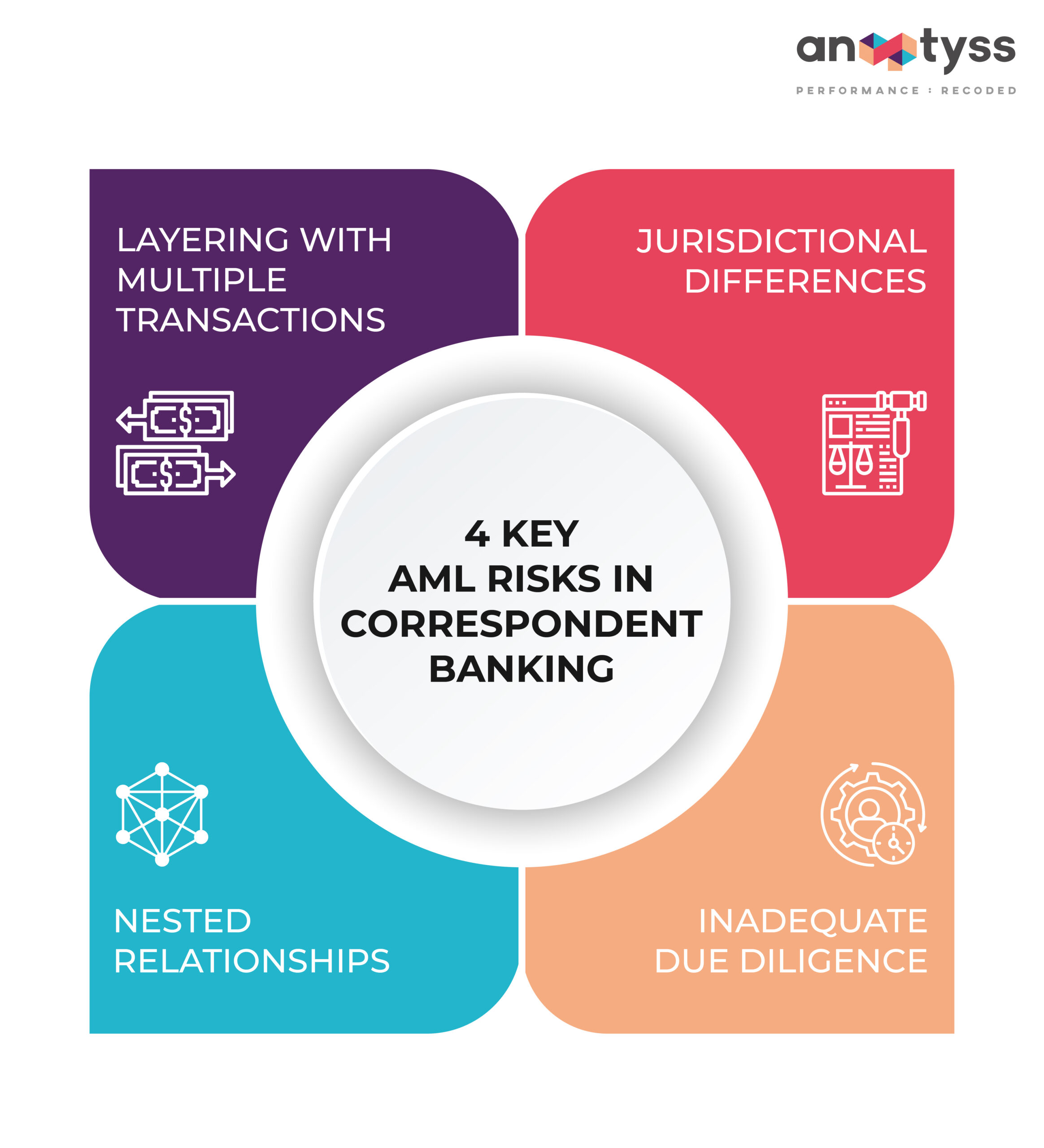
AML Risks Involved in Correspondent Banking
Despite its significance, correspondent banking is inherently susceptible to money laundering risks due to its nature of activities and cross-border transactions, which increases the complexities.
Below are some prominent factors that contribute to this vulnerability:
1. Layering with Multiple Transactions
Due to the nature of correspondent banking, the correspondent bank often lacks direct access to information about the ultimate parties involved in a transaction. This lack of transparency can be exploited for money laundering purposes.
To better understand how AML red flags manifest across channels, read our blog on FATF Red Flags for Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing.
Further, the sheer volume and complexity of transactions processed through correspondent banking networks can make it challenging to detect suspicious activities.
2. Jurisdictional Differences
Correspondent banks operate across various jurisdictions with different AML regulatory frameworks. Criminals can exploit the weaker controls in the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) systems to gain access to the international financial system.
3. Nested Relationships
Smaller banks often lack robust AML controls and access the international financial system through larger banks. This ‘nested’ arrangement of banks can further obscure the true origin and beneficiaries of funds.
4. Inadequate Due Diligence
Lack of adequate due diligence, such as insufficient customer verification, weak transaction monitoring, and efficient enterprise risk management processes, allows criminals to hide their true identity and move illicit funds through correspondent banking networks.
Real-World Examples of Correspondent Banking AML Compliance Risks
Below are a few real-world examples of AML risks in correspondent banking that lead to significant fines for major financial institutions.
HSBC faced a $1.9 billion fine in 2012 for AML lapses, including poor monitoring of money laundering through correspondent banking.
Deutsche Bank was fined $258 million in 2015 for violating US sanctions through correspondent banking activities.
UniCredit Group was subjected to a substantial $1.3 billion fine due to its involvement in processing forbidden transactions with sanctioned entities and countries like Libya, Iran, and Cuba.
More recently, in 2023, Swedbank Latvia faced a $3.4 million fine for managing transactions connected to Crimea via US correspondent banks.
4 Key Strategies to Mitigate Money Laundering Risks in Correspondent Banking
Addressing money laundering risks in correspondent banking requires a multi-faceted approach. Below are some best practices that banks can implement to minimize the risk of financial crimes, such as money laundering and terrorism financing.
1. Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Banks must conduct thorough due diligence on their direct correspondent banking clients and the customers of the clients to the best possible extent. This includes understanding the following:
- The nature of the respondent bank’s business.
- Client’s customer base.
- The jurisdictions in which the correspondent banking client operates
2. Robust Transaction Monitoring Systems
Banks can analyze suspicious patterns and flag unusual transactions using a robust monitoring system. For this, they can use:
- Advanced data analytics.
- Solutions based on intelligent technologies, such as AI and machine learning.
- Blockchain for crypto AML compliance — helps trace cryptocurrency transactions identify associated wallets and track down perpetrators.
Explore how to build a robust transaction monitoring system aligned with AML compliance best practices.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Banks and financial institutions must adhere to the regulatory frameworks and international AML standards, such as those set by regulatory authorities like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), to mitigate the AML risks associated with correspondent banking. By adhering to these regulations, banks can:
- Identify suspicious transactions
- Conduct due diligence on correspondent relationships
- Maintain a robust monitoring system
Banks and financial institutions can also follow the FATF guidelines to address the challenges and AML risks in correspondent banking.
4. Training and Awareness
Regular workforce training in detecting and reporting suspicious activities can help banks and financial institutions create awareness about the latest money laundering techniques and trends among employees and empower them to identify and address risks proactively.
Banks can leverage digital learning and knowledge management solutions, such as Fluent, to deploy and boost workforce training programs for rapid skilling with measurable outcomes.
Conclusion
Correspondent banking presents unique AML challenges to banks and financial institutions across the globe. This blog is a comprehensive overview of correspondent banking. It provides foundational knowledge, discusses risks, and suggests key strategies to mitigate the AML risks associated with correspondent banking.
See how one institution achieved a 75% reduction in false alerts in sanctions compliance using Anaptyss’ AI-powered solution, ALFA.
Anaptyss offers comprehensive financial crime compliance and fraud risks in correspondent banking. With deep domain expertise, Anaptyss employs ALFA – an advanced AI/ML-powered AML compliance solution – to strengthen anti-money laundering (AML) capabilities and navigate cross-border compliance challenges.
To learn more, write to us at: info@anaptyss.com.